
High blood pressure is common in older adults, but often goes unnoticed or untreated. In this article we explore the causes, symptoms, and treatments of hypertension. Whether you are an older adult, a caregiver, or a healthcare professional, read on for insights that can improve quality of life.
What Is Hypertension?
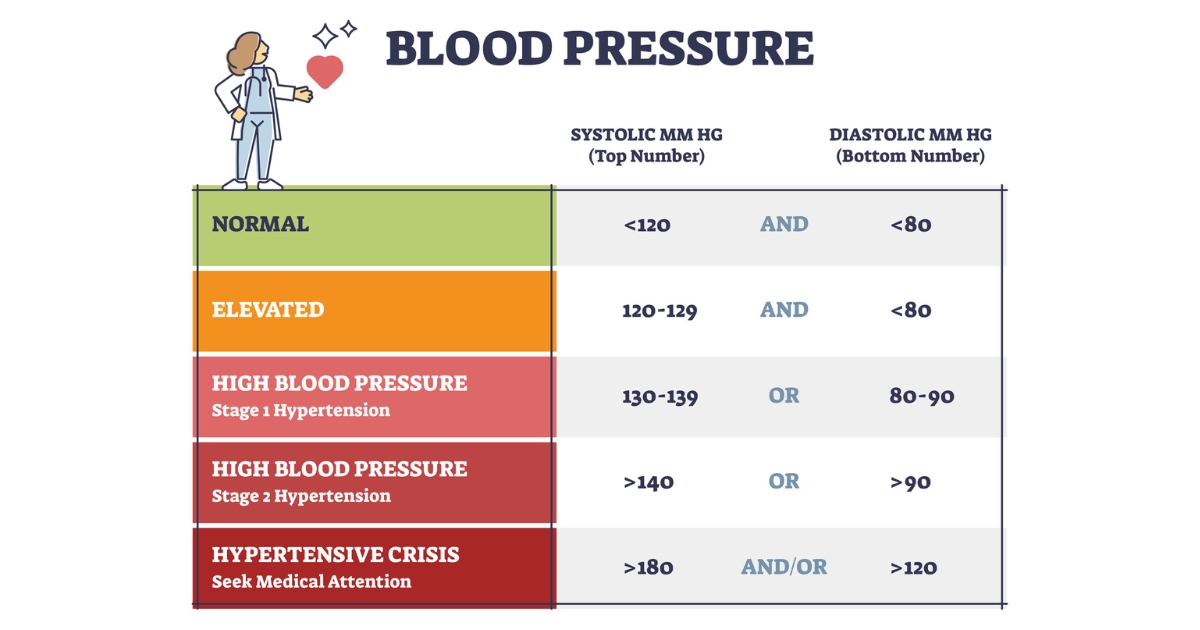
Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a condition where the force of the blood against your artery walls is consistently too high. This increased workload and pressure can lead to a host of health issues if left unmanaged. Blood pressure is measured using two values:
- Systolic Pressure: The force exerted on arteries during a heartbeat.
- Diastolic Pressure: The force when the heart is at rest between beats.
A typical reading is presented as systolic over diastolic, e.g., 120/80 mm Hg. Consistently high readings over time can indicate hypertension.
Causes of Hypertension in the Elderly
While high blood pressure can be influenced by a myriad of factors, some are especially pertinent for older adults.
Age-Related Changes
- Blood Vessel Rigidity: As we age, our blood vessels can lose their elasticity, making the heart work harder to circulate blood.
- Hormonal Changes: For women, hormonal shifts following menopause can lead to increases in blood pressure. For men, decreases in testosterone can similarly affect blood pressure levels, though the relationship isn’t fully clear.
Lifestyle Factors
- Diet: High salt intake, saturated fats, and lack of fruits and vegetables can elevate blood pressure.
- Physical Inactivity: Less exercise can lead to weight gain and reduced heart health.
- Alcohol and Tobacco Use: Chronic use can significantly raise blood pressure.
Medical Factors
- Medications: Some, like certain NSAIDs and cold remedies, can increase blood pressure.
- Coexisting Conditions: Diseases like kidney disease or sleep apnea can exacerbate hypertension.
Genetic Predisposition
If close family members have had hypertension, the likelihood increases that you may also experience it, especially as you age.

Symptoms and Warning Signs
Hypertension, often referred to as "the silent killer," can be difficult to detect due to its subtle signs. Here are key indicators to be aware of:
Common Symptoms
- Headaches, especially at the back of the head
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Blurred vision
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain
Note: Hypertension might not always manifest noticeable symptoms, making regular check-ups crucial.
Urgent Warning Signs
If you or someone you know experiences the following symptoms, seek emergency medical attention immediately:
- Severe chest pain
- Severe headache accompanied by blurred vision and confusion
- Nausea and vomiting
- Severe anxiety
- Shortness of breath
- Seizures
- Unresponsiveness
Risks and Complications
Hypertension isn't just a stand-alone issue; it is a condition that can lead to a cascade of other health problems, especially if left uncontrolled. The stakes are even higher for older adults, who may already be grappling with other health challenges.
Heart Disease and Stroke
Elevated blood pressure levels put added strain on your heart, increasing the risk of developing heart diseases like:
- Coronary artery disease
- Angina
- Heart failure
Additionally, high blood pressure is a leading risk factor for stroke, as it can cause blood vessels in the brain to burst or clog more easily.
Kidney Failure
The kidneys serve as filters for waste products in the blood. High blood pressure can damage the blood vessels in the kidneys, reducing their ability to function effectively. This can lead to kidney failure, requiring dialysis or a kidney transplant for survival.
Vision Loss
Hypertension can cause damage to the delicate blood vessels in the eyes, leading to conditions like retinopathy, macular degeneration, and even complete loss of vision in severe cases.
Cognitive Decline
Persistent high blood pressure may hinder blood flow to the brain, increasing the risk of cognitive issues like dementia and Alzheimer disease.
Peripheral Artery Disease
High blood pressure can narrow the blood vessels in the legs, arms, stomach, and head, leading to peripheral artery disease. This condition can result in pain during movement and, in extreme cases, may require surgical intervention.
Sexual Dysfunction
For men, high blood pressure can lead to erectile dysfunction by reducing blood flow to the penis. For women, it can result in decreased sexual desire and arousal issues.
Diagnosis and Monitoring
- Blood Pressure Management: Hypertension is initially identified by taking blood pressure readings. Typically, this involves a sphygmomanometer, which gauges the pressure in the arteries during heartbeats (systolic) and rests (diastolic).
- Consistent Readings: Blood pressure can vary based on factors like stress or physical activity. Thus, multiple consistent high readings over time are necessary for a diagnosis rather than a singular high measurement.
Advanced Diagnostic Tests
If your blood pressure is consistently high, further tests may be recommended to rule out underlying conditions or to assess any organ damage. These may include:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): To check for signs of heart disease.
- Echocardiogram: To get a detailed image of your heart.
- Urine Test: To check kidney function.
- Blood Tests: To check cholesterol levels, kidney function, and other important indicators.
Monitoring
- At-Home Monitoring: Home blood pressure monitors offer insights into daily fluctuations and can complement, but not replace, professional medical assessments.
- Regular Medical Check-Ups: Periodic appointments with healthcare providers are crucial for tracking hypertension progress and treatment effectiveness.
- Telemedicine: Telemedicine allows patients to have routine check-ins remotely, beneficial for those with mobility or distance challenges.

Treatment Options
Managing hypertension is a lifelong commitment, especially for older adults who are more susceptible to its harmful effects. Treatment typically involves a multi-faceted approach that combines lifestyle changes with medication.
Lifestyle Changes
- Dietary Adjustments:
- DASH Diet: The Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet is rich in vegetables, fruits, and low-fat dairy foods.
- Reduced Sodium Intake: Limiting salt can make a significant difference in blood pressure levels.
- Physical Activity: Regular physical exercise, such as walking, swimming, or light aerobic activities, can help lower blood pressure and improve overall cardiovascular health.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight can reduce the strain on your cardiovascular system.
- Alcohol and Tobacco: Moderation or elimination of alcohol and tobacco can improve your blood pressure and overall health.
- Stress Management: Techniques like deep breathing, meditation, and mindfulness can also contribute to blood pressure control.
Medications
Medications often serve as the cornerstone of hypertension treatment, particularly for those who don't achieve sufficient control through lifestyle changes alone.
- Diuretics: These help the kidneys eliminate excess salt and water from the body.
- Beta-Blockers: These reduce nerve signals to the heart and blood vessels, lowering blood pressure.
- ACE Inhibitors: These medications help relax blood vessels by reducing the level of a hormone that constricts them.
- Calcium Channel Blockers: These medications relax the muscles of the blood vessels, making them less constrictive.
- Other Medications: Other options include alpha-blockers, alpha-beta blockers, and vasodilators, among others.
Consult Keystone Health for a holistic treatment plan tailored to your needs, especially considering potential side effects and interactions with other medications you may be taking.
Once treatment has started, it is crucial to continue regular check-ups and monitoring to assess the effectiveness of your treatment plan. Adjustments may be needed over time, either to the type or dosage of medication or to the lifestyle recommendations.

Overcoming Hypertension
Aging with grace isn't about avoiding challenges; it is about managing them effectively to lead a fulfilling life. Hypertension is a common hurdle for many, but with the right approach and support, it is entirely possible to leap over it and continue on your path to a healthier, happier you.
Keystone Health offers support for older patients in Idaho by providing house calls and other forms of care. Learn more about how we can help you maintain your quality of life throughout the aging process.
